Your organization (similar to everyone else’s) holds more data now than ever before. For context, in 2024, the global data volume reached an estimated 149 zettabytes, and it’s expected to reach 181 zettabytes this year [*].
Having this much data is not the problem. But not all of it is safe.
Between remote work, cloud migration, and third-party integrations, sensitive information now moves faster and across more touchpoints than traditional security models were built to handle.
In the last quarter of 2025 alone we’ve seen hackers release 5.7 million records belonging to Qantas [*]. Discord was on the news again after the PIIs of roughly 70,000 users were leaked [*]. SonicWall made a new appearance after announcing data exposure impacting 17,000 organizations using its cloud backup service [*].
This has led to an increase in public concern on data security and privacy. The ripple effect is an uptick in the adoption of data loss prevention solutions —a market that has grown to $3.5billion in just a few years [*].
What are DLP Solutions?
DLP solutions are platforms that help you identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data across endpoints, networks, cloud-based apps, and storage environments.
They give security teams the insight to understand where critical data lives, who has access to it, and how it’s being shared. This way, they can prevent accidental leaks, ransomware attacks, unauthorized access, malicious exfiltration, or other forms of cyber threats before they happen.
Beyond protecting intellectual property (IP) and customer data, DLP plays a critical role in meeting global compliance obligations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
When you combine this with a Zero Trust approach, it helps enforce least-privilege access, monitor abnormal activity, prevent malware attacks, and maintain visibility into how sensitive data is used, shared, and stored.
What to Look for in DLP Solutions
When you’re choosing a DLP solution, your focus should be on finding a system that aligns with how your organization manages and protects data.
You’d typically want to go for platforms that provide a mix of context-aware visibility, policy flexibility, and intelligent automation that scales with your security posture.
Some other core capabilities include:
Data Discovery and Classification
This is mainly about knowing where your sensitive data resides. A strong DLP platform automatically identifies and classifies data across file shares, email systems, cloud applications, endpoints, and on-premises repositories.
This visibility helps organizations understand their data footprint and enforce the right policies before a breach ever occurs.
Some more advanced tools (like Teramind) use machine learning and content inspection to identify sensitive data, even when it’s hidden in unstructured formats such as PDFs, images, or chat logs.
Policy Creation and Enforcement
This allows you to build customizable policies that fit your business model. Whether that’s protecting financial records, customer PII (personally identifiable information), healthcare data, or intellectual property.
What you’re looking for is context-aware policies that adapt dynamically based on user role, data type, location, and risk level.
Real-Time Monitoring and Protection
A good DLP tool should provide real-time monitoring for both data in motion (as it travels across the network) and data at rest (stored on devices or servers).
This helps security teams stop unauthorized transfers or downloads before they become incidents.
In addition, look for tools that can apply automated controls such as blocking, or encrypting data based on predefined rules, reducing reliance on manual intervention.
Remediation Workflows and Incident Response
Opt for solutions that include automated remediation workflows and incident response playbooks that trigger alerts, assign cases, and guide analysts through resolution steps.
Some tools integrate directly with SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response) platforms to accelerate response time, close feedback loops, and learn from recurring incidents.
Behavior Analytics and User Insights
You don’t want false positives as they can cripple productivity. That’s why your preferred DLP platform should integrate User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) to understand how employees normally interact with data.
For example, when activity deviates from the norm, e.g., a user downloads an unusually large volume of files, the system should flag it for review or automatically restrict access.
Integration and Ecosystem Compatibility
Finally, a solid DLP solution should connect seamlessly with your broader security ecosystem, including SIEM, CASB, EDR, IAM, and threat intelligence platforms.
This is a good capability for large enterprises managing hybrid environments as it offers centralized alerting, and coordinated response across tools.
The 10 Best Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Vendors
| Tool Name | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Teramind | Behavioral DLP solution with real-time user activity monitoring (UAM) and AI-driven analytics. | Organizations needing comprehensive behavioral analysis and insider threat protection. |
| Mimecast Incydr | SaaS solution focused on insider risk detection and threat management. | Enterprises facing risks of data exposure and exfiltration by insiders. |
| Trend Micro iDLP | Integrated DLP that simplifies security by connecting with existing Trend Micro systems. | Low-cost buyers seeking quick implementation. |
| Symantec DLP | Modular enterprise data security solution with deep inspection capabilities. | Large enterprises with complex data protection needs. |
| Fortra (Digital Guardian) | Cloud-based endpoint DLP with comprehensive monitoring capabilities. | Organizations requiring military-grade data protection. |
| Trellix | Real-time data tracking and detection solution (formerly McAfee/FireEye). | Businesses needing advanced threat detection and response. |
| Forcepoint DLP | Enterprise-class DLP with global policy management and unified reporting. | Large organizations with diverse data protection requirements. |
| Proofpoint DLP | Email-focused DLP solution with strong machine learning capabilities. | Companies prioritizing email security and compliance. |
| Microsoft Purview DLP | Integrated DLP solution natively built into Microsoft 365 services. | Organizations heavily invested in the Microsoft ecosystem. |
| DTEX | Insider risk management and behavioral DLP solution. | Companies focusing on user behavior analytics and insider threats. |
1. Teramind
Teramind is a leading DLP and insider risk management platform for enterprises that need complete visibility into how data is used, accessed, and moved across their organization.
The platform combines user activity monitoring (UAM), data loss prevention, and behavior analytics into one unified solution. Once installed, it continuously tracks user actions across endpoints, applications, and networks to detect risky behavior.
Using its DLP engine for example, Teramind automatically blocks, warns, or restricts high-risk actions such as copying files to USB drives, uploading confidential data to unauthorized cloud platforms, or sharing sensitive documents via email.
Key Features
- Content-based DLP policies: Teramind allows administrators to create granular, content-aware rules that automatically detect sensitive information like PII, PHI, or financial records. These policies apply across applications, emails, and storage devices to prevent unauthorized access or transmission.
- User activity monitoring (UAM): Provides continuous visibility into user behavior, including file access, messaging, web activity, and data transfers.
- Content inspection with OCR: Teramind inspects structured and unstructured content, including images/screenshots via OCR, and supports document fingerprinting so you can track files even when renamed or modified
- Behavioral anomaly detection: Teramind’s analytics engine establishes behavioral baselines for each user and flags deviations that may indicate insider threats or policy violations.
- Session recording and forensic playback: Users can record all monitored sessions, including screen activity, keystrokes, file transfer, keystrokes etc.
Use Cases
- Insider threat detection: Organizations can use Teramind to monitor user activities in real time, detecting anomalies such as unauthorized file transfers or unusual access to sensitive data.
- Endpoint data protection: Companies can deploy Teramind on employee devices to prevent confidential files (like customer lists or IP) from being copied to USB drives or sent via personal emails.
- Compliance monitoring: Highly regulated sectors (finance, healthcare) can rely on Teramind’s behavior analytics and policy enforcement to ensure GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS compliance.
What Are Customers Saying About Teramind?
- Excellent product with a wide range of use cases.
- No limits on what you can track!
- The ultimate solution for remote team management
- Excellent for a remote working setup.
2. Mimecast Incydr (formerly Code42 Incydr)
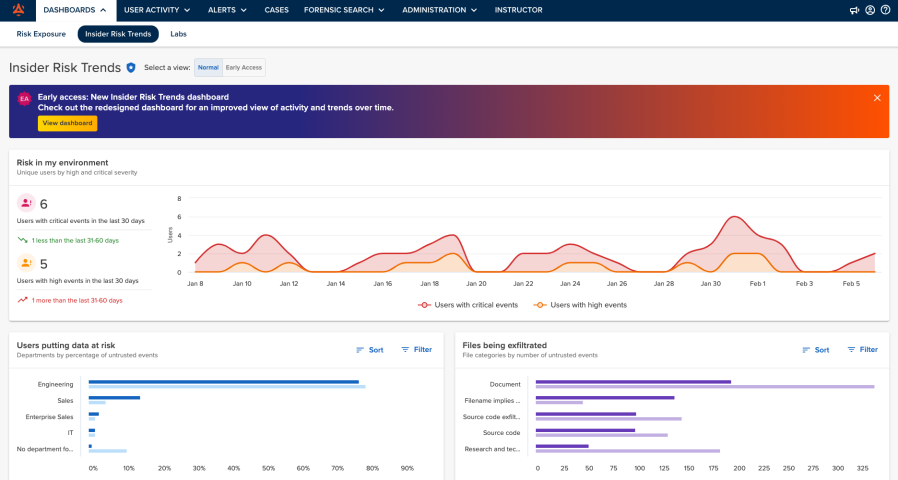
Mimecast Incydr is a cloud-native data protection and insider-risk management platform that focuses on stopping data loss or theft from within the organization. It does this by emphasizing context and behaviour —i.e., who is moving the data, where it’s going, how this compares to expectations.
The engine behind this approach is the PRISM (Proactive Risk Identification & Severity Model). It uses over 250 indicators across three‐dimensional risk indicators: data context (e.g., file sensitivity, location), user context (e.g., role, history, behavior) and destination context (e.g., upload location, cloud service), to score and prioritise events so that the most critical incidents surface quickly.
Mimecast Incydr also supports automated remediation workflows such as blocking uploads, revoking permissions, launching training modules to users who trigger risky actions.
And because of its design for rapid deployment and cloud scale, it offers a more agile approach. This makes it a good option for enterprises aiming for faster time-to-value while controlling sensitive data in the cloud and at the endpoint.
Key Features
- Watchlists and targeted high-risk user controls: Users can create “watchlists”, i.e., groups of users who warrant elevated monitoring (e.g., contractors, departing employees, senior IP-holders). They can also apply specific controls (blocking, tighter monitoring) to those groups.
- Exfiltration controls: Incydr monitors browser uploads, clipboard-paste actions, unsanctioned cloud app usage and sync behaviour.
- Micro-training: When Incydr detects a risky behavior, it automatically triggers responses such as blocking the action, sending tailored micro-training to the user, quarantining the file, or escalating to a case in the SOC workflow.
Use Cases
- Employee offboarding risk management: Before or during employee exits, Incydr can track data access and transfers to ensure no confidential files leave the organization.
- Cloud collaboration oversight: Companies can use it to monitor data sharing across Google Drive, Slack, or Microsoft 365, spotting unsafe behaviors in real time.
3. Trend Micro iDLP
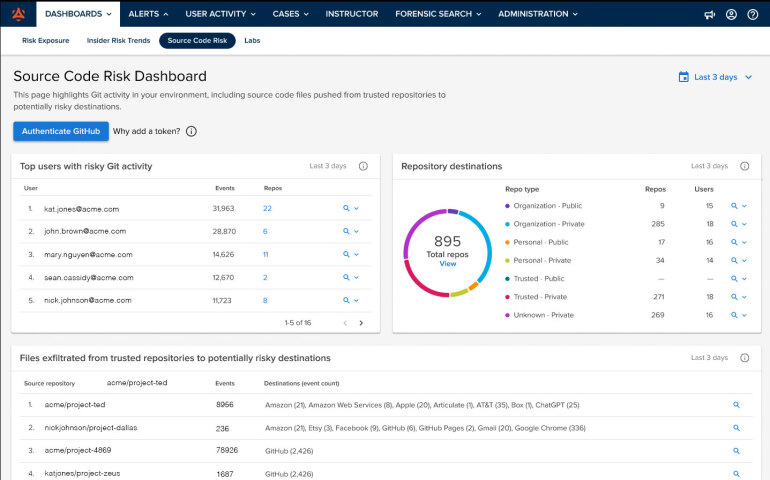
Trend Micro’s iDLP offering is designed to give enterprises a lightweight yet integrated option for data loss prevention. This is good if you want to extend DLP controls across endpoints, networks, and cloud without deploying a completely separate infrastructure.
The solution is built to protect sensitive and proprietary data in motion(via USB drives, email, cloud uploads), in use (copy, print, screenshot on endpoint) and at rest (file shares, archives) while leveraging the broader Trend Micro security ecosystem—e.g., the company’s Apex One endpoint agent or OfficeScan Data Protection Service.
Key Features
- Granular device control: Users can set rules based on removable device vendor and serial number (USB drives, CD/DVD writers, other media). This enables blocking or restricting specific devices rather than all removable media.
- Pre-built compliance templates: Comes with out-of-the-box templates (PCI DSS, HIPAA, GLBA, US PII etc.), plus international data-identifier patterns you can extend or customize.
- Centralised management via Trend Micro control manager: Policies, events, reporting and configuration across the iDLP modules and other Trend Micro products are unified under one console.
Use Cases
- Industry-specific data protection: Financial institutions can use IDLP to detect exposure of SWIFT codes, credit card numbers, and IBANs. Healthcare providers can also use it to configure policies to protect PHI under HIPAA.
- Securing data during cloud migration: During digital transformation, sensitive workloads often move from on-prem servers to cloud environments. IDLP helps by inspecting and classifying files during migration, ensuring no private data is exposed or uploaded to non-compliant repositories.
4. Symantec DLP
Symantec DLP (now part of Broadcom Inc’s cybersecurity portfolio), is another solution that gives organizations full visibility and control over sensitive data across their endpoints, networks, storage, and cloud environments.
It offers a unified console and policy framework. With this, security teams can define one set of rules and workflows that apply across endpoints, network, cloud and storage.
There’s also advanced detection capabilities such as content inspection, pattern matching (regex), fingerprinting, OCR, and contextual analysis of user behaviour and data movement.
Key Features
- EDM and IDM:
- EDM (Exact Data Matching): This allows the system to fingerprint an exact dataset (e.g., a database of customer records) and then monitor for those exact values in motion, at rest, or in use.
- IDM (Indexed Document Matching): This is used to index large volumes of documents (for example engineering drawings, contracts, IP-documents) and then detect if those documents (or portions of it ) appear in places they shouldn’t.
- ICA (Information-Centric Analytics): This module uses analytics and user/entity behaviour context to help prioritise risky events and reduce false positives.
- Offline and remote device coverage: For devices that are off-network or remote, the endpoint agent continues to enforce policies, monitor data in use (USB, copy/paste, print) and block high-risk actions.
Use Cases
- Enterprise-wide policy enforcement: Global enterprises can use Symantec DLP to centrally define and enforce data protection policies across endpoints, servers, and networks.
- Data protection in complex hybrid clouds: Symantec DLP integrates with cloud APIs and network monitors to maintain visibility and control over data regardless of storage location.
5. Fortra DLP (formerly Digital Guardian)
Forta DLP is a SaaS solution that primarily focuses on granular control of sensitive data at the endpoint level. It covers laptops, desktops, and other devices where data is created, used, moved or stored on- or off-network.
The platform deploys a lightweight agent on endpoints that monitors data (in use, at test, and in motion). It then records detailed metadata about every data event including file creation, copying, uploads, print operations, and removable-media activity.
Plus, since it operates close to the OS level, it can capture fine-grained details about what users do, the applications involved, and where the data is going.
Key Features
- Adaptive data protection policies: The solution applies protection based on risk levels, user roles, and business context. For example, a policy might allow engineers to transfer CAD files within an internal domain but automatically encrypt or block the same files if transferred externally.
- Centralized management console: All endpoint agents feed into a unified management console, where administrators can define policies, monitor incidents, and generate compliance reports.
- Granular endpoint controls: This gives administrators full control over how users interact with data. It can block file transfers to USBs, restrict print operations, limit uploads to unsanctioned cloud apps, and enforce encryption for specific file categories.
Use Cases
- Intellectual property and design file protection: R&D-heavy firms (like semiconductor or automotive companies) can use Fortra to identify, tag, and restrict access to sensitive file types such as CAD drawings, design specs, and formulas.
- Managed DLP-as-a-Service for resource-limited teams: Fortra offers a managed DLP model that continuously tunes policies based on observed data flows. This can help smaller security teams maintain enterprise-grade protection without the operational overhead.
6. Trellix DLP
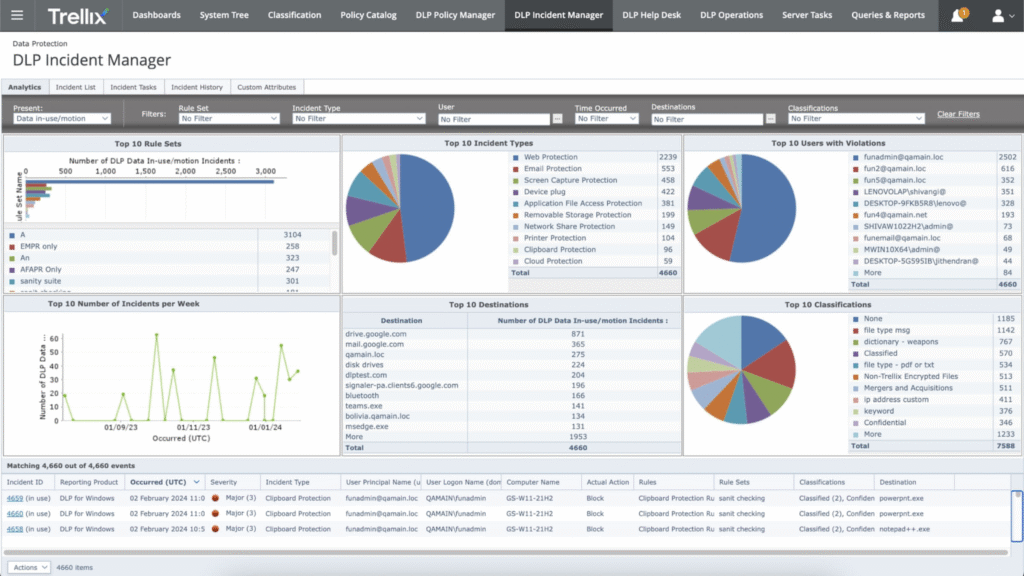
Trellix DLP (formed from McAfee + FireEye) is an enterprise data protection platform that detects, classifies, and secures sensitive data at every stage of its lifecycle. It combines data fingerprinting, machine learning classification, and policy-based controls to prevent unauthorized access or exfiltration
It also integrates deeply with the company’s broader cybersecurity ecosystem, including Trellix EDR/XDR, ENS (Endpoint Security), and Trellix ePO (ePolicy Orchestrator) for centralized management. This enables organizations to unify data protection, endpoint defense, and threat detection into one adaptive framework.
Key Features
- Device control: This restricts removable media use, Bluetooth transfers, and other risky vectors that might enable data exfiltration.
- ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO): Administrators can define, deploy, and manage DLP policies across endpoints, networks, cloud apps, and email gateways from a single console.
- Cloud and web integration: Trellix DLP extends protection into cloud environments through integrations with CASB solutions and APIs for services like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, Box, and Salesforce. It ensures the same data policies apply whether data resides on-premises or in the cloud.
Use Cases
- Real-time risk analytics: Trellix leverages ML to establish baselines of normal user activity and detect deviations. This can help detect insider misuse or compromised accounts attempting data theft.
- Anomaly detection: Organizations can use Trellix DLP to restrict or encrypt data written to removable media, ensuring USB drives or external disks can’t be used for covert data transfers.
7. Forcepoint DLP
Forcepoint DLP is an enterprise security solution designed to prevent sensitive information from being accidentally exposed, maliciously stolen, or misused.
It combines content inspection, machine learning, and user behavior analytics (UBA) to identify and prevent data leaks across endpoints, networks, cloud apps, and email systems.
The platform is built on the Forcepoint ONE Security Service Edge (SSE), integrating with Forcepoint CASB, SWG, and ZTNA modules. This gives enterprises a unified platform to secure data wherever users work (office, at home, or in the cloud).
Key Features
- ContentIQ engine: Offers a large base of over 1,700 classifiers, policy templates covering 80+ countries and 90+ regulations, and supports hundreds of file types, NLP scripts and image-OCR based detection.
- Risk-adaptive protection (RAP): Uses native analytics to evaluate user behavior, context and data-interaction patterns (over 130 indicators of behavior noted) to dynamically adjust the risk level of users and actions.
- Advanced data discovery and forensics: Enables organizations to scan storage repositories (on-premises and cloud) to locate sensitive data, tag owners and create audit trails.
Use Cases
- Responsive risk analysis: If a user’s risk score rises due to unusual activity, Forcepoint can automatically increase restrictions, such as disabling data transfers or encrypting sessions.
- Intent-based adaptive DLP: Forcepoint is great at analyzing user intent —e.g., legitimate file share and a malicious attempt to leak data. This can help organizations respond with adaptive policies like warning pop-ups for accidental violations or automatic blocking for risky behaviors.
8. Proofpoint DLP
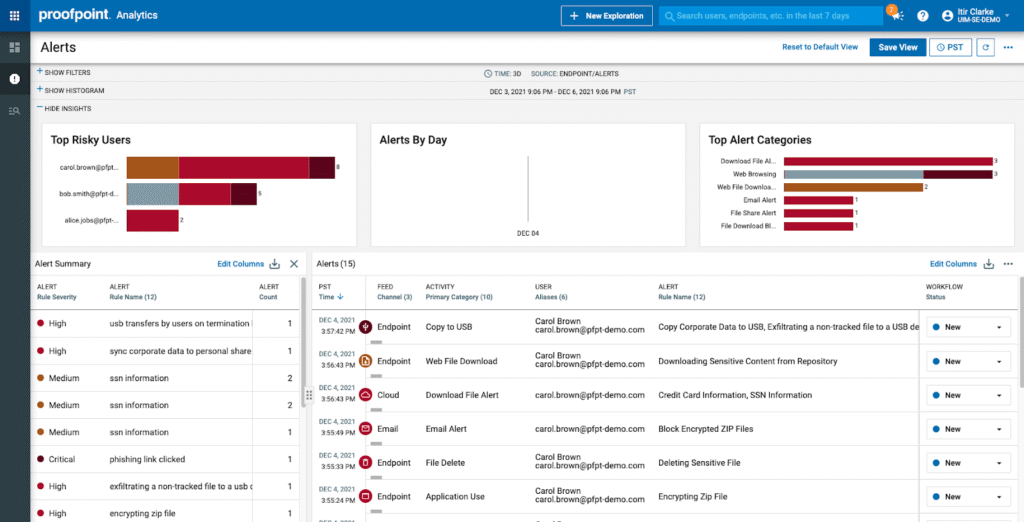
Proofpoint DLP positions itself as a ‘people-centric,’ cloud-native solution for protecting cloud applications, endpoints, emails, and on-premises repositories. The vendor combines user behaviour telemetry and threat intelligence to understand how people are interacting with the data in the network.
The idea is to adopt adaptive controls that reflect how people actually use and share information. In this case, monitoring file and data movements (uploads, downloads, email attachments, cloud shares), while correlating those actions with user context (role, behaviour, device) and threat context (compromised account, phishing event).
For example, Proofpoint’s email‐DLP component scans outbound email messages and attachments for regulated data patterns, custom dictionaries, or company-specific identifiers.
Key Features
- Rich detector library: Proofpoint provides extensive pre-built detectors (smart identifiers, regex, fingerprinting, OCR) and classification engines, plus support for custom dictionaries.
- Insider threat management (ITM): Provides visibility into user intent through session recording, behavioral baselining, and forensics, helping teams distinguish between mistakes and malicious acts.
- Audit-ready reporting: Detailed audit logs, incident snapshots, and activity playback allow analysts to reconstruct how data left the organization and demonstrate compliance during audits. Reports can be customized for regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or industry frameworks such as ISO 27001.
Use Cases
- Email data leakage prevention: Protects outbound email communications by scanning attachments and message bodies for sensitive or regulated content.
- Integrated insider risk program: With Proofpoint’s people-centric approach, security teams can identify users with high data movement tendencies, deliver targeted training, or enforce stricter controls for those segments.
9. Microsoft Purview DLP
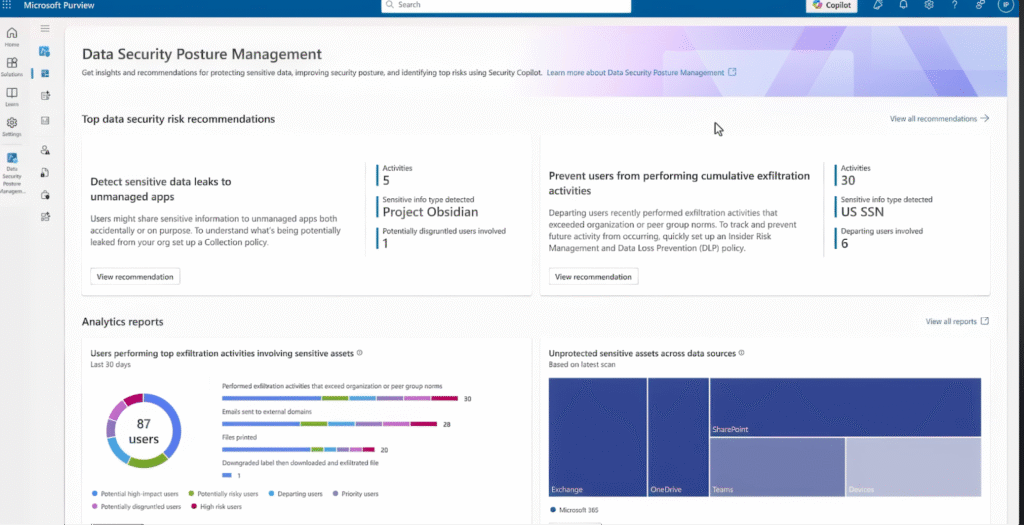
Microsoft Purview DLP is a unified, cloud-native data protection solution built into the Microsoft 365 ecosystem and extended across endpoints, on-premises repositories, and third-party cloud environments.
It’s designed to identify, monitor, and automatically protect sensitive data within Office apps, email, Teams, SharePoint, OneDrive, and even non-Microsoft services via connectors.
The Purview DLP leverages Microsoft’s Information Protection framework, which combines data classification, sensitivity labeling, and policy-based controls.
When it detects sensitive content (like PII, financial data, or confidential business files), it applies the appropriate protection. This could be blocking sharing, encrypting data, restricting downloads, or simply warning users in real time.
Key Features
- Policy tips: Because it’s part of Microsoft’s productivity stack, users receive policy tips directly within familiar interfaces like Outlook, Word, or Teams, helping them make informed security decisions without disrupting workflow.
- Cloud App Governance and Endpoint DLP: Through Defender for Cloud Apps and Defender for Endpoint, Purview extends visibility to unmanaged devices and third-party cloud environments. Endpoint DLP monitors actions like copying data to USBs, printing, or uploading to personal drives, ensuring consistent protection even off-network.
- Automated incident response: When a violation occurs, Purview DLP logs detailed event metadata (user, file, action, sensitivity, location) and can automatically trigger incident workflows, alert administrators, or escalate to Microsoft Sentinel for SIEM correlation.
Use Cases
- Audit Automation: Purview helps compliance teams automatically generate reports demonstrating alignment with frameworks like GDPR or ISO 27001.
- Cross-cloud DLP integration: Purview integrates with Windows Defender and third-party apps to prevent data leaks across devices and hybrid cloud systems.
10. DTEX
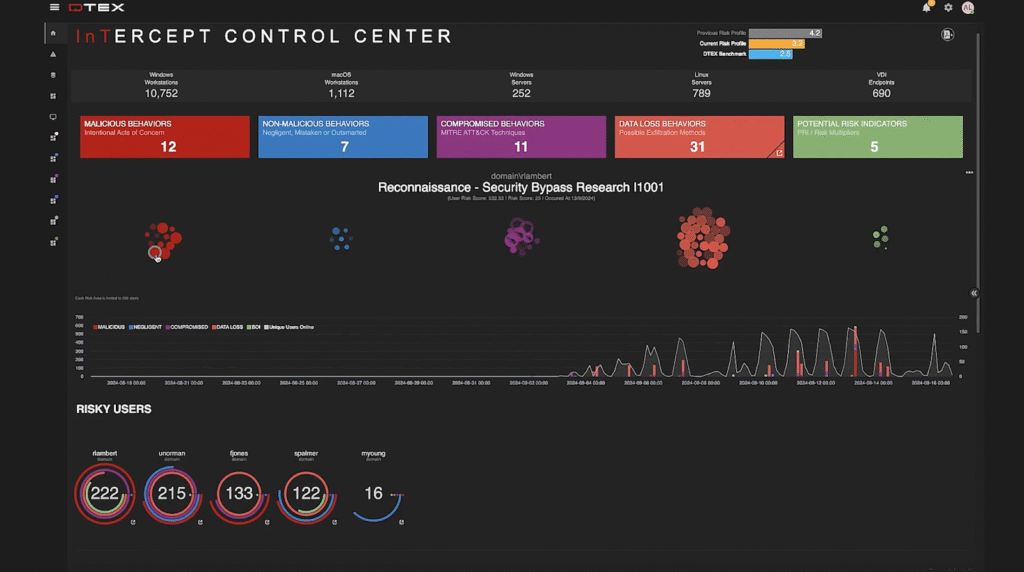
DTEX focuses on human behavior visibility, understanding why data is being moved or accessed before it ever leaves the environment.
The platform continuously collects anonymized endpoint telemetry at scale, covering user activity such as file creation, copying, network connections, process launches, and peripheral use.
Then it processes this data in real time through its DTEX InTERCEPT Behavioral Datalake, which applies advanced analytics and machine learning to identify patterns of risk. This allows organizations to detect malicious insiders, compromised accounts, or negligent employees before data exfiltration occurs.
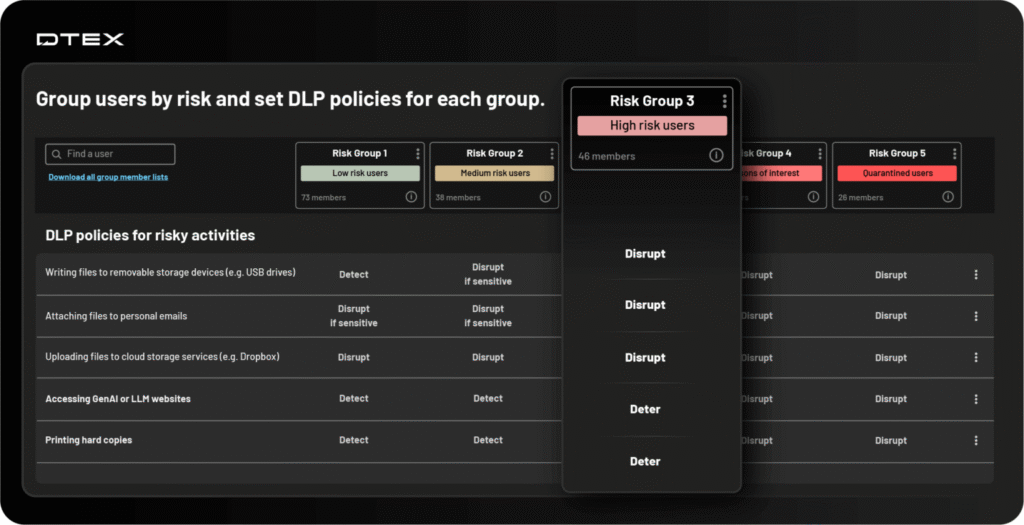
Key Features
- Timeline reconstruction: InTERCEPT records complete user activity timelines, enabling security teams to reconstruct events leading to a policy violation or insider incident.
- Exfiltration detection: The platform tracks all data interactions (including copy-paste, print, screenshot, USB transfer, and cloud uploads), correlating them with user behavior to detect anomalies that signal potential leaks or misuse.
- Intent modeling: uses predictive analytics to determine intent. If a user begins showing signs of exfiltration, e.g., archiving large files or connecting unauthorized devices, the system escalates risk scores proactively.
Use Cases
- Pre-exfiltration detection: It continuously collects endpoint telemetry to profile normal user behavior, flagging deviations that signal insider risk or data misuse.
- Preserving workforce visibility: DTEX anonymizes behavioral data, allowing organizations to monitor and mitigate insider risks while maintaining employee privacy.
The State of DLP In 2026
The future of DLP is being reshaped by how and where organizations handle data.
Information is no longer confined to on-premises servers. Now, it’s flowing freely between cloud apps, hybrid workspaces, and remote devices.
And here’s how it’s all going to unfold in 2026:
Growing Role of AI and Machine Learning
Traditional DLP relied heavily on keyword matches and rigid policy rules, which limited scalability and accuracy for large enterprises.
Meanwhile, with AI and machine learning, DLP is becoming more adaptive and predictive. Modern systems can now learn from user behavior, detect intent, and identify risks before data leaves the environment.
They correlate unusual actions with risk signals and automatically trigger real-time responses. This level of automation reduces false positives and lightens the workload for already stretched security teams.
Shift Toward Cloud-native and SaaS-first DLP Solutions
According to Gartner, by 2026, over 70% of enterprise data will reside in cloud platforms and SaaS applications [*]. This trend is pushing more organizations to embrace multi-cloud infrastructures and remote collaboration.
As such, modern DLP tools are being designed to accommodate this reality. The goal is to provide unified visibility across endpoints, cloud apps, email, and web gateways without heavy on-premises infrastructure.
Behavior Analytics and Insider Risk Management
Human behavior remains the most unpredictable variable in cybersecurity, and also the biggest source of data breaches. Studies show that roughly 95% of successful cyber-attacks are as a result of human error [*].
The new generation of DLP solutions puts user intent and behavior analytics at the core of their design. They believe by understanding normal activity patterns, they can identify when something changes. This way, organizations can catch risks early, coach employees in real time, and build a security-aware culture.
The Impact of Zero Trust, Encryption, and Real-Time Monitoring
Zero Trust replaces the assumption of trust with continuous verification. This is to ensure that every user, device, and data movement is validated.
Encryption is becoming the final safeguard. Regardless of the stage (in transit, in use, and at rest), it ensures that even if an attacker or insider gains access, the data remains unreadable and unusable.
When you combine all of this with real-time visibility into how data flows across the enterprise, it creates a security posture where prevention and detection are seamless.
See the Risk Before It Happens. Stop It with Teramind.
Teramind combines user behavior analytics, content-based DLP, and real-time policy enforcement, giving you complete visibility into how information moves across your organization.
And if your business handles customer data, Teramind gives you the confidence that it’s always protected. It automatically stops sensitive files from leaving approved channels, flags insider threats before they escalate, and builds a transparent audit trail for every interaction for audit and compliance.
Preventing data loss can be a bit difficult. How about we predict it… and stop it— with Teramind?
| See why leading enterprises trust Teramind to protect what matters most. View Teramind’s Live Demo → |
How To Select the Best DLP Tool for Your Organization
When selecting the best DLP tool for your organization, it’s essential to consider several factors to ensure that the solution aligns with your security needs and business objectives.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the steps and considerations involved:
- Understand Your Data. Before choosing a DLP tool, it’s crucial to clearly understand the types of data your organization handles. Identify where your data resides, how it moves within and outside your organization, and its sensitivity level. This will help you determine the scope and scale of the DLP solution needed.
- Define Your Data Protection Goals. Outline what you aim to achieve with a DLP tool. Goals may include protecting intellectual property, complying with regulations (like GDPR and HIPAA), or preventing data breaches. Clearly defined goals will guide your choice of features and capabilities in a DLP tool.
- Evaluate Key Features. Different DLP tools offer various features, and selecting the right tool depends on the features that best meet your needs. Essential features to consider include:
- Content discovery. Ability to scan and identify sensitive data across various locations.
- Data monitoring. Real-time monitoring of data usage and movement.
- Incident response and alerts. Automated responses and alerts for policy violations.
- Integration capabilities. Compatibility with your existing security tools and IT infrastructure.
- Ease of policy enforcement. Tools should facilitate straightforward policy creation and enforcement.
- Consider Deployment Options. DLP solutions can be deployed on-premises, in the cloud, or as a hybrid model. Each option has its pros and cons:
- On-premises. It offers control over the physical infrastructure but requires significant maintenance and upfront costs.
- Cloud-based. It provides scalability and lowers initial costs but may raise concerns about data sovereignty and security.
- Hybrid. It combines the benefits of both on-premises and cloud, making it suitable for organizations transitioning to the cloud.
- Assess Compliance Requirements. Ensure that the DLP tool you choose helps you meet the regulatory requirements relevant to your industry. The tool should facilitate compliance with laws and standards regarding data protection and privacy.
- Vendor Reputation and Support. Research potential vendors’ reputations, focusing on their stability, customer support, and the robustness of their security measures. Vendor support is crucial, as it affects the implementation phase and ongoing maintenance of the DLP system.
- Test and Evaluate. Before making a final decision, testing the DLP tools on your shortlist in your environment is advisable. Pilot testing will help you see how well each tool integrates with your systems and meets your expectations.
- Cost Consideration. Analyze the total ownership cost, including licensing, implementation, training, and maintenance costs. Opt for a tool that offers the best value for money within your budget.
- User Reviews and Feedback. Look at feedback from other users, especially those in similar industries. User reviews can provide insights into the real-world effectiveness of a DLP tool and highlight any potential issues or advantages you might not have considered.
DLP Solution FAQs
Which is the best DLP?
The best DLP (Data Loss Prevention) software depends on your organization’s needs and requirements. Some popular DLP solutions include Teramind DLP, Trellix, and Forcepoint DLP. It is recommended to evaluate different options based on features such as data identification, prevention capabilities, ease of use, and integration capabilities with your existing security infrastructure.
What does DLP software do?
DLP software, or Data Loss Prevention software, helps organizations protect sensitive data by monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized access or data leaks. It enables businesses to define policies, monitor user activity, and take immediate action to mitigate the risk of data breaches or loss.
What is an example of DLP?
An example of DLP (Data Loss Prevention) software is Teramind DLP, which offers data identification, prevention capabilities, and integration with existing security infrastructure. Teramind is a popular choice for organizations looking to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
What are the three types of DLP?
The three types of DLP (Data Loss Prevention) software are network, endpoint, and cloud. Network DLP monitors and protects data while it is in transit over the network, endpoint DLP secures data on individual devices, and cloud DLP protects data stored in cloud-based applications and services.
What are DLP risks?
DLP risks refer to potential vulnerabilities and threats that organizations may face regarding data loss prevention. Such risks can include unauthorized access or sharing of sensitive data, breaches, non-compliance with regulations, and loss of business reputation. Implementing robust DLP software can help mitigate these risks and protect organizations from data loss incidents.
What are common DLP use cases?
Some common DLP use cases include protecting intellectual property, securing customer data, and preventing insider threats. DLP software helps organizations prevent data leaks and unauthorized access to sensitive information and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
What can DLP block?
DLP software can block unauthorized access to sensitive data, prevent data leaks, and enforce policies to ensure compliance with industry regulations. Additionally, it can block the sharing of confidential information via email, USB drives, or cloud storage.


